Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Create a Sound Composer project#
The Sound Composer is a tool that allows you to generate the sound of a system by combining the sounds of its components, which we call sources here. Each source can be made of data coming from test analysis, or from a simulation, or simply consist of a single audio recording. The sources are combined into a Sound Composer project, where each source is assigned to a track.
A track is a data structure made of a source data, a source control data, an output gain, and, optionally, a transfer function in the form of a digital filter (which models the transfer from the source to the listening/recording position). It can generate the sound of the component (as characterized by the source data), in specific operating conditions (the source control), and filtered according to the transfer function.
This example shows how to create a Sound Composer project, with the SoundComposer class.
It first creates a new project, then adds tracks to it, and finally generates the sound of the
project.
The example shows how to perform these operations:
Create a project,
Create a track with a source of type Harmonics, and add it to the project,
Create a track with a source of type Spectrum, and add it to the project,
Generate the signal of the project,
Display the spectrogram of the generated signal,
Save the project as an .scn file.
Set up analysis#
Setting up the analysis consists of loading the required libraries, connecting to the DPF server, and downloading the data files required in this example.
from ansys.sound.core.examples_helpers import (
download_sound_composer_FRF_eMotor,
download_sound_composer_source_control_eMotor,
download_sound_composer_source_control_WindRoadNoise,
download_sound_composer_source_eMotor,
download_sound_composer_source_WindRoadNoise,
)
# Load Ansys libraries.
from ansys.sound.core.server_helpers import connect_to_or_start_server
from ansys.sound.core.signal_processing import Filter
from ansys.sound.core.sound_composer import (
SoundComposer,
SourceBroadbandNoise,
SourceControlTime,
SourceHarmonics,
Track,
)
from ansys.sound.core.spectrogram_processing import Stft
# Connect to a remote DPF server or start a local DPF server.
my_server, my_license_context = connect_to_or_start_server(use_license_context=True)
# Download the necessary files for each source considered in this exeample: the source file
# containing the acoustic definition of the source, the control profile file containing the
# operating conditions of the source (engine or vehicle speed over time), and optionally the FRF
# file containing the source's transfer function.
path_sound_composer_source_eMotor = download_sound_composer_source_eMotor(server=my_server)
path_sound_composer_sourcecontrol_eMotor = download_sound_composer_source_control_eMotor(
server=my_server
)
path_sound_composer_FRF_eMotor = download_sound_composer_FRF_eMotor(server=my_server)
path_sound_composer_source_WindRoadNoise = download_sound_composer_source_WindRoadNoise(
server=my_server
)
path_sound_composer_sourcecontrol_WindRoadNoise = (
download_sound_composer_source_control_WindRoadNoise(server=my_server)
)
Create a new Sound Composer project#
To create a new Sound Composer project, instantiate the SoundComposer class.
Sources will be combined as tracks into this instance, allowing you to generate the sound of the
project.
sound_composer_project = SoundComposer()
Let us give the new project a name.
sound_composer_project.name = "Electric vehicle interior sound"
Create track #1 for the e-motor source#
To model the noise of the e-motor, we create a track with a harmonics source, which contains the harmonics of the e-motor noise. The track also contains a source control that defines the operating conditions of the e-motor, and a filter that represents the transfer function of the e-motor noise source to the receiver point, usually the driver position.
Create a new Sound Composer track, meant as a recipient for the e-motor data.
track_eMotor = Track(name="eMotor harmonics noise")
Create a harmonics source, using the SourceHarmonics class, passing the path to the
source file as an argument. This file contains the levels of the harmonics of the e-motor noise
for several engine speed values.
source_eMotor = SourceHarmonics(file=path_sound_composer_source_eMotor)
Create a source control profile, using the SourceControlTime class.
This source control profile defines the operating conditions of the e-motor, here the speed of
the e-motor, increasing from 250 to 5000 rpm in 8 seconds.
source_control_eMotor = SourceControlTime(file_str=path_sound_composer_sourcecontrol_eMotor)
Create a filter, using the Filter class.
This filter models the transfer function (FRF) of the e-motor noise source to the receiver point.
filter_eMotor = Filter(file=path_sound_composer_FRF_eMotor)
Assign created objects to the track.
# Assign the source control to the source.
source_eMotor.source_control = source_control_eMotor
# Assign the source to the track.
track_eMotor.source = source_eMotor
# Assign the filter to the track.
track_eMotor.filter = filter_eMotor
Add the track to the Sound Composer project. It is the first track of this project.
sound_composer_project.add_track(track_eMotor)
Create track #2 for the wind and road noise source#
To model the wind and road noise produced in the cabin while driving, we create a track with a broadband noise source, whose spectrum envelope changes according to change in the speed of the vehicle over time.
Create a new Sound Composer track, meant as a recipient for the wind and road noise data.
track_WindRoadNoise = Track(name="Wind and road noise")
Create a broadband noise source, using the SourceBroadbandNoise class.
source_WindRoadNoise = SourceBroadbandNoise(file=path_sound_composer_source_WindRoadNoise)
Create a source control profile, using the SourceControlTime class. This source control
describes the change of vehicle speed over time.
source_control_WindRoadNoise = SourceControlTime(
file_str=path_sound_composer_sourcecontrol_WindRoadNoise
)
Assign created objects to the track.
# Assign the source control to the source.
source_WindRoadNoise.source_control = source_control_WindRoadNoise
# Assign the source to the track
track_WindRoadNoise.source = source_WindRoadNoise
Add the track to the Sound Composer project. It is the second track of this project.
sound_composer_project.add_track(track_WindRoadNoise)
Generate the signal of the project#
Now, let us generate the signal of the project using the SoundComposer.process() method.
This method generates, for each track, the acoustic signal of the source, filters it with the
associated filter, if any, and applies the track gain, and finally sums all resulting tracks’
signals together.
Generate the signal of the project, using a sampling frequency of 44100 Hz.
sound_composer_project.process(sampling_frequency=44100.0)
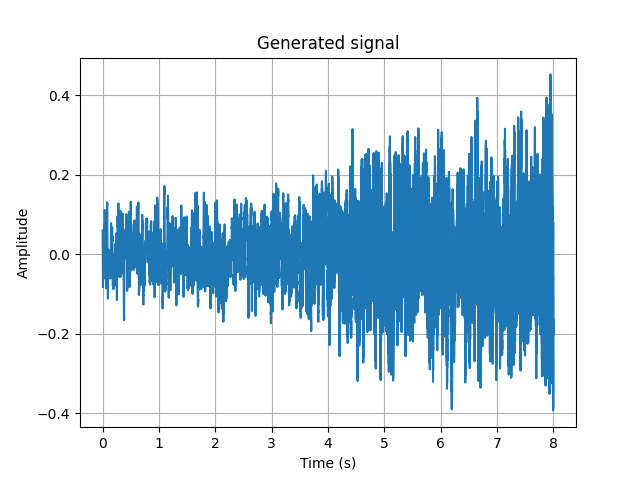
Display the generated signal using the SoundComposer.plot() method.
sound_composer_project.plot()
Use the built-in print() function to display a summary of the content of the project.
print(sound_composer_project)
SoundComposer object: "Electric vehicle interior sound" (2 track(s))
Track 1: SourceHarmonics, "eMotor harmonics noise", gain = +0.0 dB
Track 2: SourceBroadbandNoise, "Wind and road noise", gain = +0.0 dB
Retrieve the resulting signal as a DPF Field object.
generated_signal_from_project = sound_composer_project.get_output()
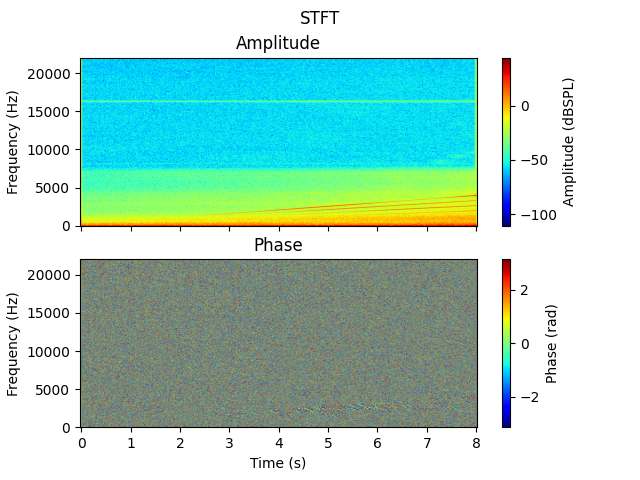
Display the spectrogram of the generated signal using the Stft class.
spectrogram = Stft(signal=generated_signal_from_project)
spectrogram.process()
spectrogram.plot()
Save the entire Sound Composer project#
You can save the Sound Composer project for later use, using the SoundComposer.save()
method. This saves the project into a file with the extension “.scn” (Sound Composer project
file). This file can be loaded in Ansys Sound Analysis & Specification.
sound_composer_project.save(project_path="My_SoundComposer_Project.scn")
Conclusion#
This workflow allows you to analyze and listen to the sound of an e-motor, in realistic conditions, that is, including the background noise inside the cabin.
By analyzing the spectrogram, you can anticipate how some harmonic tones from the e-motor may be perceived by the passengers in the cabin.
Further investigations can be conducted, using other tools included in PyAnsys
Sound, such as modules Standard levels,
Psychoacoustics and
Spectral processing.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 23.076 seconds)

