Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Calculate psychoacoustic indicators#
This example shows how to calculate psychoacoustic indicators. The following indicators are included:
Loudness of stationary sounds according to ISO 532-1.
Loudness of time-varying sounds, according to ISO 532-1.
Monaural and binaural loudness of stationary sounds according to ISO 532-2.
Sharpness according to Zwicker and Fastl, “Psychoacoustics: Facts and models”, 1990.
Sharpness according to Zwicker and Fastl, over time.
Sharpness according to DIN 45692.
Sharpness according to DIN 45692, over time.
Roughness and roughness over time according to Daniel and Weber, “Psychoacoustical Roughness: Implementation of an Optimized Model, 1997.
Fluctuation strength according to Sontacchi, “Entwicklung eines Modulkonzeptes für die psychoakustische Geräuschanalyse under MatLab”, 1998.
The example shows how to perform these operations:
Set up the analysis.
Calculate indicators on loaded WAV files.
Get calculation outputs.
Plot some corresponding curves.
Set up analysis#
Setting up the analysis consists of loading the required libraries, and connecting to the DPF server.
# Load standard libraries.
import os
# Load Ansys libraries.
from ansys.sound.core.examples_helpers import download_accel_with_rpm_wav, download_flute_wav
from ansys.sound.core.psychoacoustics import (
FluctuationStrength,
LoudnessISO532_1_Stationary,
LoudnessISO532_1_TimeVarying,
LoudnessISO532_2,
Roughness,
Sharpness,
SharpnessDIN45692,
SharpnessDIN45692OverTime,
SharpnessOverTime,
)
from ansys.sound.core.server_helpers import connect_to_or_start_server
from ansys.sound.core.signal_utilities import LoadWav
# Connect to a remote DPF server or start a local DPF server.
my_server, my_license_context = connect_to_or_start_server(use_license_context=True)
Load the WAV files used in this example#
Load the signals from WAV files using the LoadWav class. They are returned as a list of
Field objects, where each field corresponds to a channel.
# Load a first signal from a WAV file: recording of a flute.
path_flute_wav = download_flute_wav(server=my_server)
wav_loader = LoadWav(path_flute_wav)
wav_loader.process()
signal_flute = wav_loader.get_output()[0]
# Load another signal from a WAV file: recording of an acceleration inside a car cabin.
path_accel_wav = download_accel_with_rpm_wav(server=my_server)
wav_loader = LoadWav(path_accel_wav)
wav_loader.process()
signal_car_acceleration = wav_loader.get_output()[0]
# Note: This signal contains a second field (RPM profile) that is useless in this example.
# Get file names, for later use.
file_name_flute = os.path.basename(path_flute_wav)
file_name_car_acceleration = os.path.basename(path_accel_wav)
Calculate ISO 532-1 loudness for a stationary sound#
Create a LoudnessISO532_1_Stationary object, set its signal, and compute the loudness
according to standard ISO 532-1.
loudness_ISO532_1_stationary = LoudnessISO532_1_Stationary(signal=signal_flute)
loudness_ISO532_1_stationary.process()
Get the ISO 532-1 loudness (in sone) and loudness level (in phon).
loudness_ISO532_1_sone = loudness_ISO532_1_stationary.get_loudness_sone()
loudness_ISO532_1_level_phon = loudness_ISO532_1_stationary.get_loudness_level_phon()
print(
f"\nThe ISO 532-1 loudness of sound file {file_name_flute} is "
f"{loudness_ISO532_1_sone:.1f} sones "
f"and its loudness level is {loudness_ISO532_1_level_phon:.1f} phons."
)
The ISO 532-1 loudness of sound file flute.wav is 39.6 sones and its loudness level is 93.1 phons.
Plot the ISO 532-1 specific loudness, that is, the loudness at each Bark band index.
loudness_ISO532_1_stationary.plot()
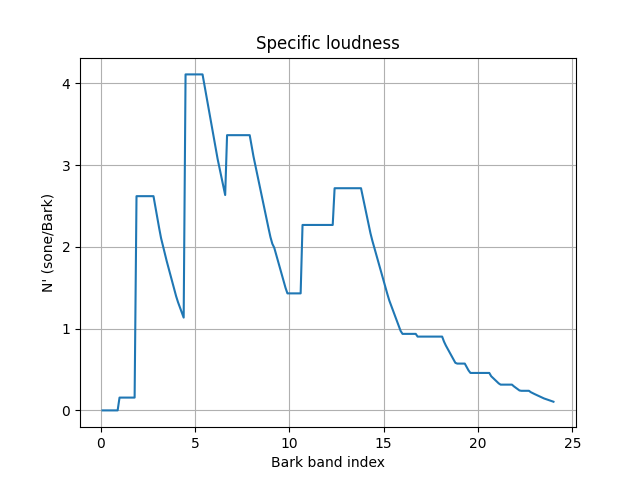
Calculate ISO 532-1 loudness for a time-varying sound#
Create a LoudnessISO532_1_TimeVarying object, set its signal, and compute the loudness.
loudness_ISO532_1_time_varying = LoudnessISO532_1_TimeVarying(signal=signal_car_acceleration)
loudness_ISO532_1_time_varying.process()
Get percentile loudness and loudness level values.
N5 = loudness_ISO532_1_time_varying.get_N5_sone()
N10 = loudness_ISO532_1_time_varying.get_N10_sone()
L5 = loudness_ISO532_1_time_varying.get_L5_phon()
L10 = loudness_ISO532_1_time_varying.get_L10_phon()
print(
f"\nThe sound file {file_name_car_acceleration} has the following percentile "
f"loudness and loudness level values:\n"
f"- N5 = {N5:.1f} sones.\n"
f"- N10 = {N10:.1f} sones.\n"
f"- L5 = {L5:.1f} phons.\n"
f"- L10 = {L10:.1f} phons."
)
The sound file accel_with_rpm.wav has the following percentile loudness and loudness level values:
- N5 = 16.4 sones.
- N10 = 15.6 sones.
- L5 = 80.4 phons.
- L10 = 79.6 phons.
Plot the ISO 532-1 loudness as a function of time.
loudness_ISO532_1_time_varying.plot()
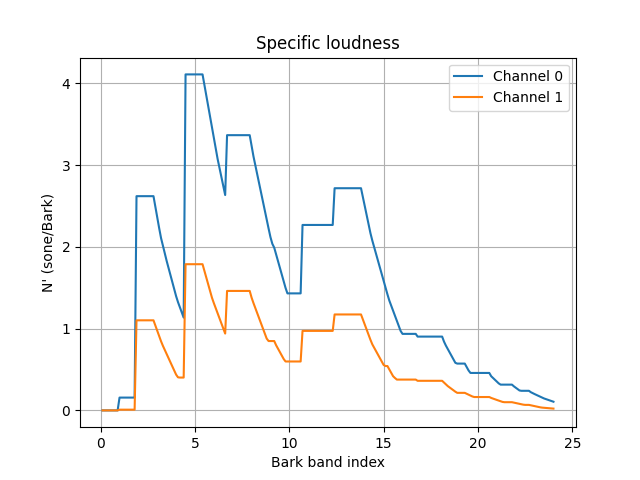
Calculate ISO 532-2 loudness for a stationary sound#
Create a LoudnessISO532_2 object, set its signal, and compute the loudness
according to standard ISO 532-2.
loudness_ISO532_2 = LoudnessISO532_2(signal=signal_flute, field_type="Free")
loudness_ISO532_2.process()
Get the ISO 532-2 binaural and monaural loudness (in sone), and loudness level (in phon).
loudness_ISO532_2_sone_monaural = loudness_ISO532_2.get_monaural_loudness_sone()[0]
loudness_ISO532_2_phon_monaural = loudness_ISO532_2.get_monaural_loudness_level_phon()[0]
loudness_ISO532_2_sone_binaural = loudness_ISO532_2.get_binaural_loudness_sone()
loudness_ISO532_2_phon_binaural = loudness_ISO532_2.get_binaural_loudness_level_phon()
print(
f"\nThe ISO 532-2 loudness of sound file {file_name_flute} is:\n"
f"\tMonaural loudness and loudness level: {loudness_ISO532_2_sone_monaural:.1f} sones, "
f"{loudness_ISO532_2_phon_monaural:.1f} phons.\n"
f"\tBinaural loudness and loudness level: {loudness_ISO532_2_sone_binaural:.1f} sones, "
f"{loudness_ISO532_2_phon_binaural:.1f} phons."
)
The ISO 532-2 loudness of sound file flute.wav is:
Monaural loudness and loudness level: 28.2 sones, 87.7 phons.
Binaural loudness and loudness level: 42.3 sones, 93.2 phons.
For comparison, display the values previously obtained with the ISO 532-1 standard. The two standards rely on similar auditory principles but differ in the way they estimate the loudness.
print(
f"\nThe ISO 532-1 loudness of sound file {file_name_flute} is "
f"{loudness_ISO532_1_sone:.1f} sones "
f"and its loudness level is {loudness_ISO532_1_level_phon:.1f} phons."
)
The ISO 532-1 loudness of sound file flute.wav is 39.6 sones and its loudness level is 93.1 phons.
Plot the ISO 532-2 binaural specific loudness, that is, the binaural loudness at each center frequency of equivalent rectangular bandwidth (ERB).
loudness_ISO532_2.plot()
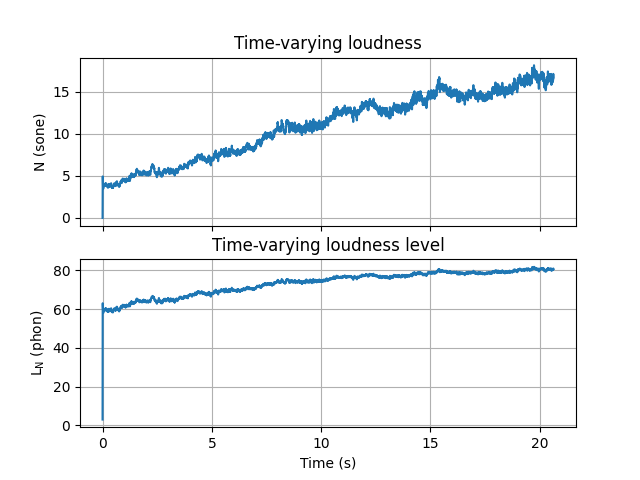
Calculate sharpness, roughness, and fluctuation strength#
Calculate the sharpness.
sharpness = Sharpness(signal=signal_flute, field_type="Free")
sharpness.process()
sharpness_value = sharpness.get_sharpness()
Calculate the sharpness over time and plot it.
sharpness_over_time = SharpnessOverTime(signal=signal_flute, field_type="Free")
sharpness_over_time.process()
sharpness_over_time.plot()
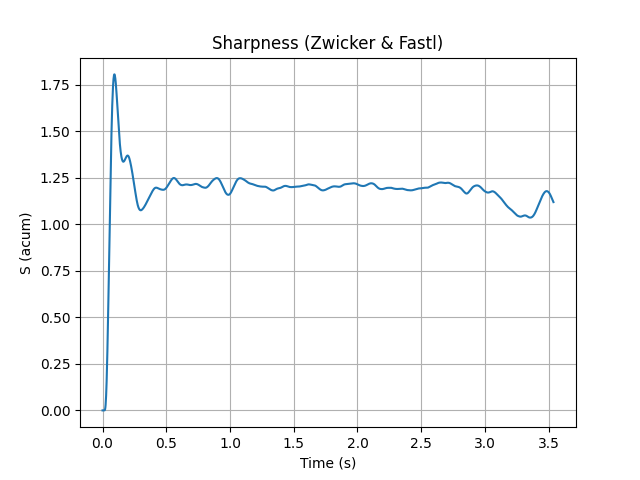
Calculate the sharpness according to standard DIN 45692.
sharpness_DIN45692 = SharpnessDIN45692(signal=signal_flute, field_type="Free")
sharpness_DIN45692.process()
sharpness_DIN45692_value = sharpness_DIN45692.get_sharpness()
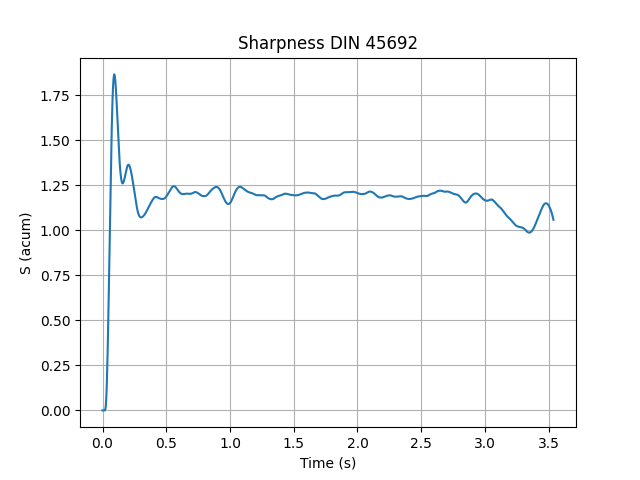
Calculate the sharpness according to standard DIN 45692, over time, and plot it.
sharpness_DIN45692_over_time = SharpnessDIN45692OverTime(signal=signal_flute, field_type="Free")
sharpness_DIN45692_over_time.process()
sharpness_DIN45692_over_time.plot()
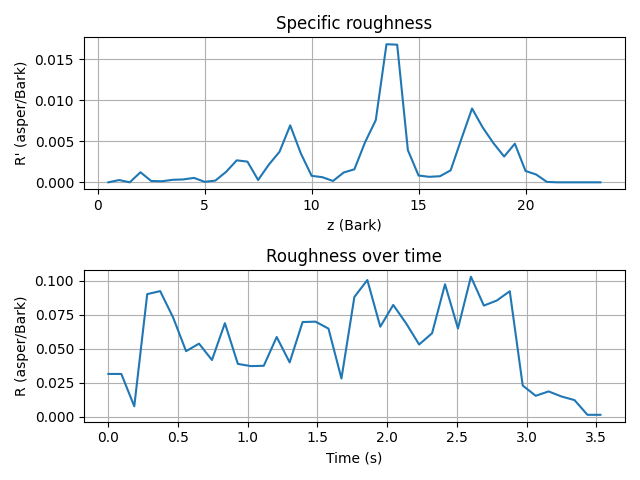
Calculate the roughness, and plot the specific roughness and roughness over time.
# Calculate the specific roughness, the roughness over time, and the overall roughness.
roughness = Roughness(signal=signal_flute)
roughness.process()
roughness_value = roughness.get_roughness()
# Plot the specific roughness and the roughness over time.
roughness_over_time = roughness.get_roughness_over_time()
roughness.plot()
Calculate the fluctuation strength.
fluctuation_strength = FluctuationStrength(signal=signal_flute)
fluctuation_strength.process()
fluctuation_strength_values = fluctuation_strength.get_fluctuation_strength()
Print the calculated indicators.
print(
f"\nThe sharpness of sound file {file_name_flute} "
f"is {sharpness_value:.2f} acum,\n"
f"its sharpness according to DIN 45692 is {sharpness_DIN45692_value:.2f} acum,\n"
f"its roughness is {roughness_value:.2f} asper,\n"
f"and its fluctuation strength is {fluctuation_strength_values:.2f} vacil."
)
The sharpness of sound file flute.wav is 1.19 acum,
its sharpness according to DIN 45692 is 1.20 acum,
its roughness is 0.06 asper,
and its fluctuation strength is 0.60 vacil.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 18.032 seconds)

